Global warming is a major environmental issue that is affecting the entire planet, and Africa is no exception. The effects of global warming on Africa are particularly severe and are likely to become even more so in the coming years.
One of the most significant effects of global warming on Africa is an increase in temperature. Average temperatures in Africa have already risen by about 1.5 degrees Celsius over the past century, and are expected to continue rising at an alarming rate. This temperature increase leads to several negative impacts, including more frequent and severe heat waves, droughts, and wildfires.
The consequences of these weather events can be devastating for African communities. Drought, for example, can lead to food shortages and malnutrition, as crops fail and livestock dies. This can have serious health impacts, particularly for children and the elderly. In addition, droughts can lead to conflicts over scarce resources, such as water and land.
Another major effect of global warming on Africa is an increase in sea levels. Rising sea levels are already causing flooding and erosion in coastal areas, and this is likely to become more widespread in the future. In addition, higher sea levels can lead to the contamination of freshwater supplies and the destruction of ecosystems, such as mangroves and coral reefs.
One of the most vulnerable regions in Africa to the effects of global warming is the Sahel, a semi-arid region that stretches across the continent just below the Sahara Desert. The Sahel is already prone to drought and food shortages, and global warming is likely to exacerbate these problems. In addition, the Sahel is home to millions of people who rely on agriculture and livestock for their livelihoods, and the impacts of global warming on these sectors could be devastating.
In addition to the direct effects of global warming, Africa is also at risk from several indirect impacts. For example, global warming is likely to lead to more frequent and severe storms and hurricanes, which can cause significant damage to infrastructure and communities. In addition, global warming is likely to lead to the spread of diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, as the warmer temperatures provide a more favorable environment for the transmission of these diseases.
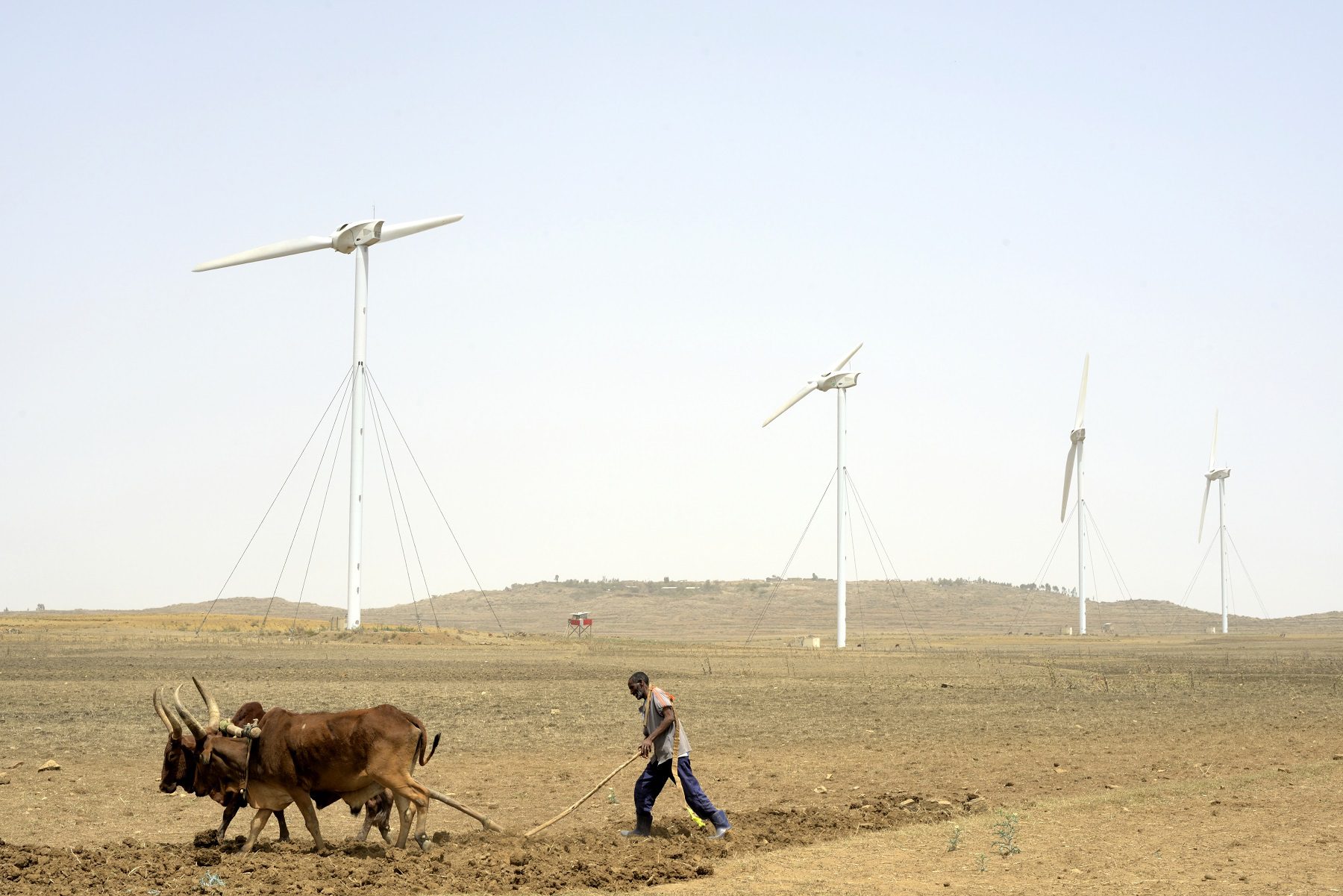
Several steps can be taken to mitigate the effects of global warming on Africa. One of the most important is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which are the main cause of global warming. This can be done through a variety of measures, such as increasing the use of renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting more sustainable land use practices.
Another important step is to adapt to the impacts of global warming that are already occurring or are expected to occur. This can involve building more resilient infrastructure to extreme weather events, such as sea walls to protect against flooding and drought-resistant crops to help mitigate the impacts of drought. It can also involve developing early warning systems and emergency response plans to help communities prepare for and respond to extreme weather events.
In conclusion, the effects of global warming on Africa are already severe and are likely to become even more so in the coming years. From rising temperatures and sea levels to more frequent and severe weather events, the impacts of global warming are wide-ranging and far-reaching. It is therefore essential that action is taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to help African communities adapt to the impacts of global warming.
Image from: https://ideas4development.org